2024 Workspace Upgrade: Step-by-Step Guide for the Optimal Monitor Positioning
Fixated on monitor screens for hours, you may experience sore muscles, headaches, discomfort, or eye strain. Whether you work in an office or take a new work-from-home mode, choosing a more ergonomic setup to fit your body proportions is the most effective way to improve posture for healthier working. The first thing you can do is to set the monitor to a proper position. There are some tips to help achieve a comfortable situation.
Why ergonomic monitor position important?
Discomfort in office settings can stem from various factors, with poor ergonomics being a significant contributor. Ergonomics plays a crucial role in ensuring the well-being and productivity of individuals, especially in the context of office work where people spend long hours at their desks. Consistently adopting static or awkward postures can be the most prominent leading to discomfort and potential injuries over time.
Positioning the monitor correctly within a computer workstation is crucial to prevent the operator from adopting awkward and uncomfortable postures. When the monitor is improperly placed, individuals often find themselves tilting their chin upwards, while bending their head and upper body forwards or sideways. These forced positions not only cause discomfort but also increase the risk of developing work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs). Additionally, a poorly located monitor can lead to various adverse effects such as eye irritation, blurred vision, dry and burning eyes, and headaches, collectively known as eyestrain.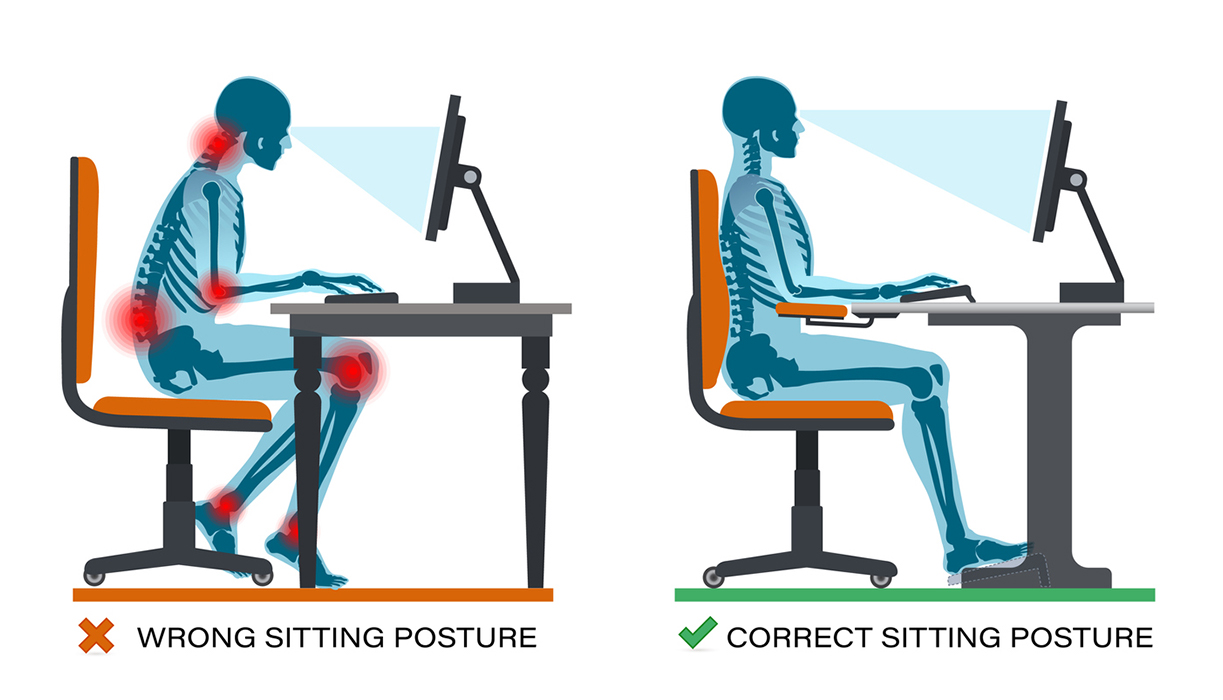
Ensuring proper ergonomic positioning of monitors is crucial for enhancing physical comfort, preserving visual health, and maximizing productivity in the workplace. This minor adjustment can yield substantial long-term advantages for both individuals and organizations.
What is the correct monitor position?
First, we should learn about two factors that decide the proper position of the monitor: viewing angle and viewing distance. The viewing angle refers to the angle formed above or below an imaginary horizontal line from the viewer's eye level to the center of the screen being observed during computer work. Meanwhile, viewing distance is the distance between the operator's eyes and the screen. Incorrect angles can result in discomfort in the neck and shoulders, while improper distances may lead to eyestrain.
Guidelines on viewing angle and distance vary, so they shouldn't be rigid rules but rather starting points for individual adjustments. There are helpful tips to check whether you have a healthy viewing position.
1. Viewing Angle
· 15 to 30 Degrees Viewing Angle
Experts concur that our eyes naturally tend to rest in a forward and downward direction. Research results vary, indicating this downward cast to be between approximately 15 to nearly 30 degrees. Delving into specifics, positioning your screen should ideally fall within the range from eye level to 30 degrees below your line of sight.
It is remarkably simple to adjust the angle at which you view your computer monitor to reduce eye strain and discomfort. It is correct that when viewing the screen, your eyes naturally rest on the browser's address bar. If not, you find your eyes naturally resting on elements like the trash bin or upper toolbar instead of the address bar, which indicates that your viewing angle might not be optimal.
· 10 to 20 Degrees Tilt Back
To accommodate your gaze, tilt the monitor slightly back about 10 to 20 degrees.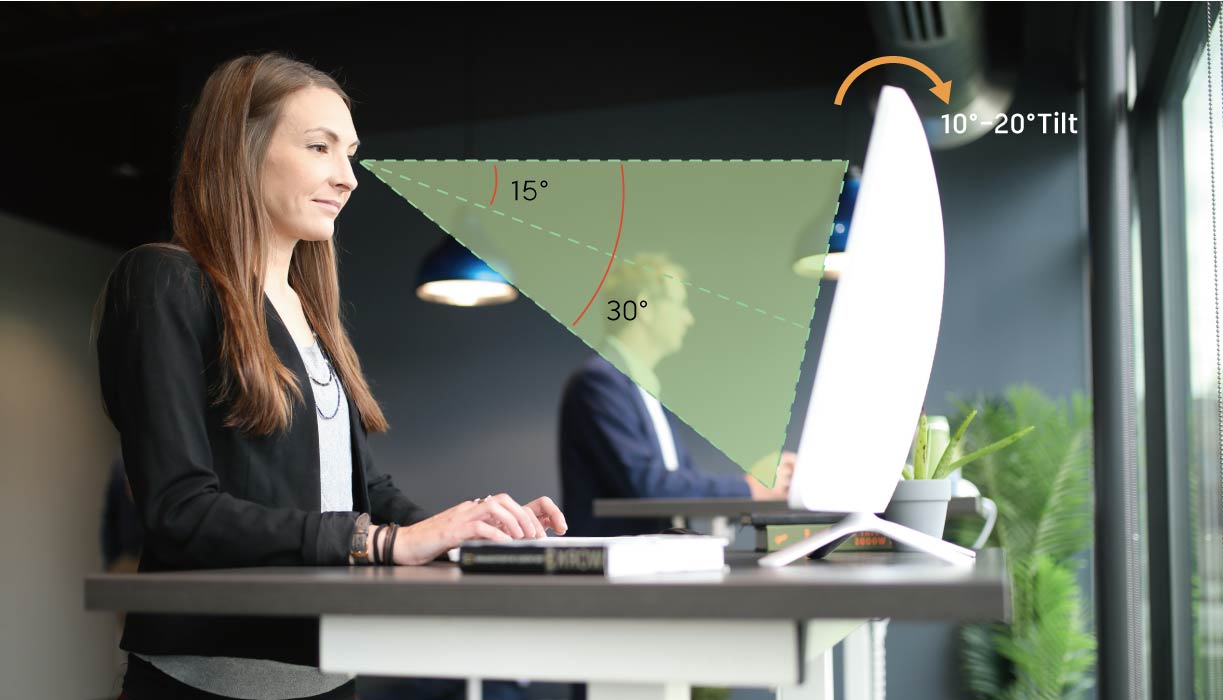
【Note】 To enhance comfort while using corrective lenses for reading or close work (such as bi-focals, tri-focals, and progressive lenses), consider positioning the monitor slightly below eye level. This adjustment may alleviate the need to tilt the head excessively to view the screen by utilizing the lower portion of the lens designed for close vision.
2. Viewing Distance
To ensure an optimal viewing distance, it's important to consider factors like ocular accommodation and convergence, which can lead to eye strain when too close to a screen. To avoid such issues, achieving the right distance is key. When positioning yourself in front of a computer monitor, extend your arm fully and place the screen at that exact distance.
Given the variability in computer screen sizes, it's essential to confirm that the monitor isn't positioned either too close or too far away. With the correct setup, you should be able to comfortably view the entire screen without straining your eyes or needing to adjust your posture.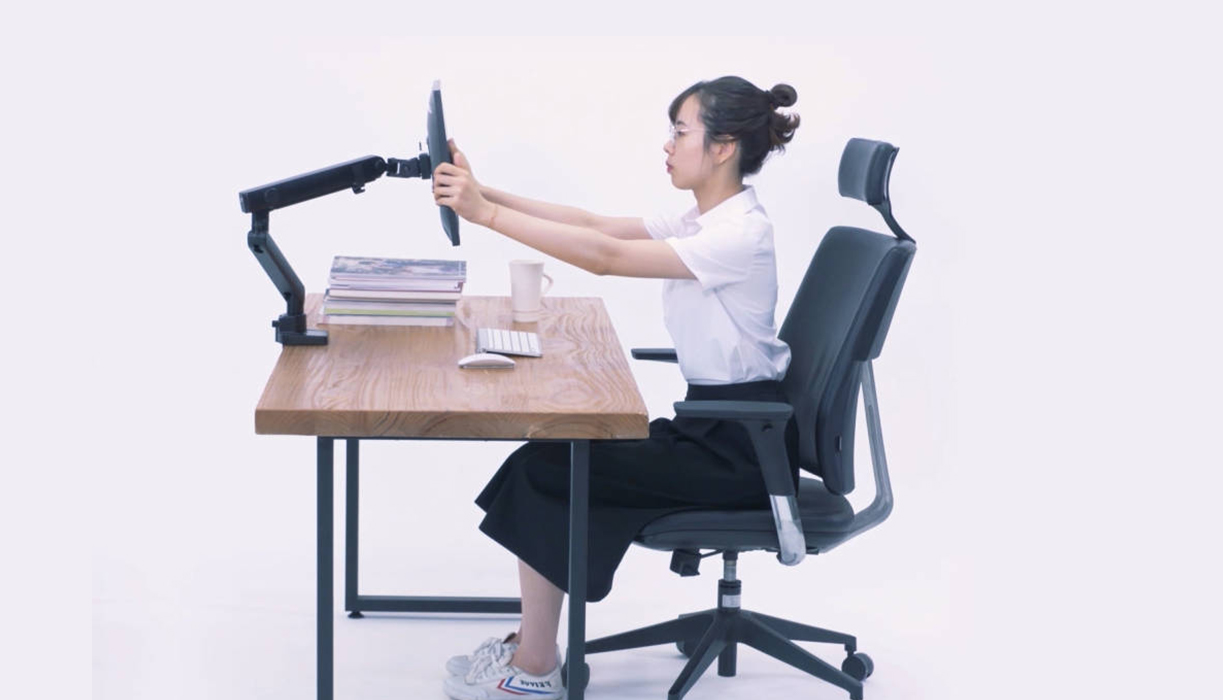
3. Multi-Screen
Dual monitor arms offer a distinct advantage over basic ergonomic monitor stands by accommodating two screens instead of just one. In professional settings, the use of dual monitors has become increasingly common due to the productivity gains they offer. Studies have shown that using two monitors can enhance user performance, providing an experience similar to that of a single ultra-wide monitor.
When setting up two or more monitors, ensure they are positioned as closely as possible with their inside edges touching. Additionally, tilt the monitors slightly inwards for better viewing. From an ergonomic standpoint, proper positioning, viewing distance, and angle are crucial for both single and dual-monitor setups. However, the arrangement of dual monitors depends on the user's usage pattern.
· Both Screens Are Used Equally
They should be positioned straight ahead at an arm's length distance. Keep yourself, keyboard, and mouse in the middle of the dual monitors for balanced accessibility.
· Primarily Use One Monitor More Than the Other
The emphasis should be placed on the primary monitor's positioning, following standard viewing distance guidelines. The secondary monitor can follow similar rules but may be angled slightly to favor the user's dominant eye.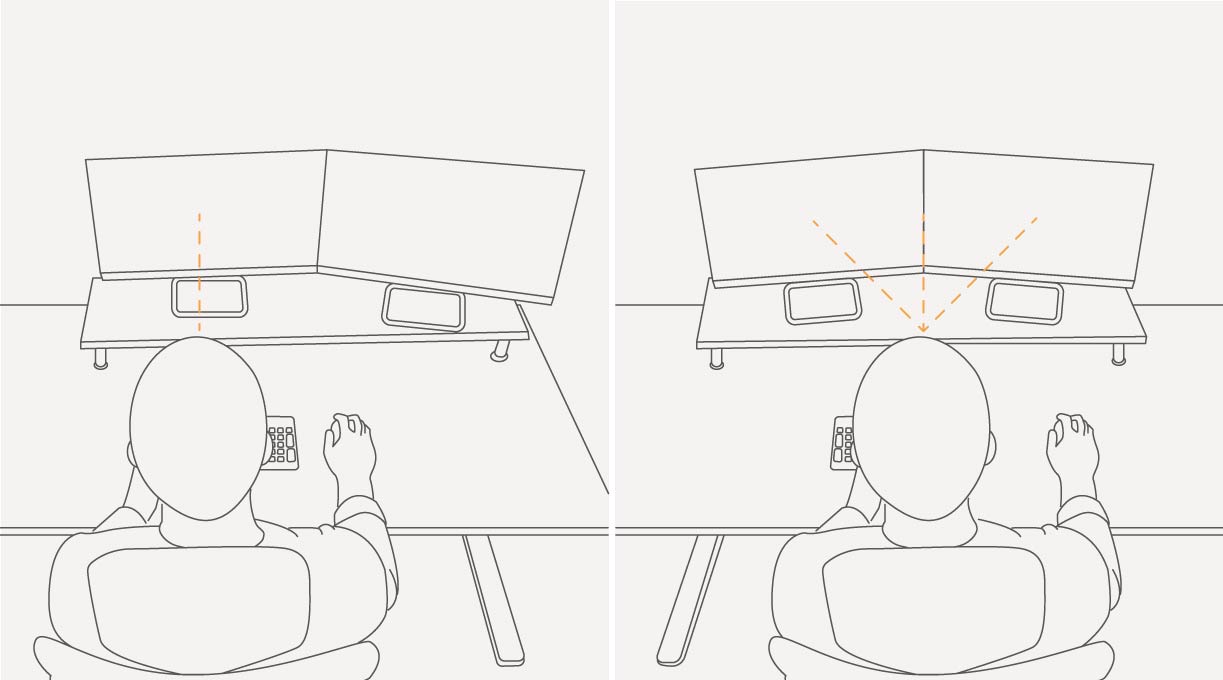
Best Ways to Set Your Monitor to The Ideal Position
It is the most flexible way to mount a monitor. A monitor arm allows you to easily adjust the height, tilt, and angle of your monitor with just a few simple movements. You can easily swivel the monitor to share your screen with others or to switch between landscape and portrait orientation. This not only helps reduce neck and eye strain but also frees up valuable desk space.
A desktop riser or stand elevates your monitor to eye level, promoting better posture and reducing the strain on your neck and shoulders. It also creates additional storage space underneath the monitor to keep your desk organized and clutter-free. In terms of adjustability, you can choose a fixed riser or height adjustable one to fit your needs.
Covert the standard desk into height adjustable healthy helper. Effortlessly customize your preferred height for ergonomic comfort and reduced strain during extended work sessions. With perfect monitor placement, bid farewell to sedentary habits and embrace productivity, turning any desk into a healthier, more active workstation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prioritize ergonomic monitor positioning for a healthier, more productive workspace. With tools like monitor arms, desktop risers, and desk converters, achieving optimal setup is simple. Say goodbye to discomfort and hello to efficiency. Invest in your well-being today for a better work experience.







